anti windup gain
Integral Anti-Windup for PI Controllers Fig. To comprehensively evaluate the effect of saturation on the system performance L -norm is further introduced and then the anti-windup compensator is designed based on H 2 H performance of the constrained closed-loop.

The Anti Windup Scheme With The Pi D Controller In Automatic Reset Download Scientific Diagram
Therefore an additional LMI constraint is also employed to guarantee the robustness.

. Integral windup also known as integrator windup or reset windup refers to the situation in a PID feedback controller where a large change in setpoint occurs say a positive change and the integral term accumulates a significant error during the rise windup thus overshooting and continuing to increase as this accumulated error is unwound offset by errors in the other. Using the parameter-dependent Lyapunov function and the parameter-dependent sector condition a nonconvex synthesis condition is first obtained for the LPV system with actuator saturation. Conditional integration The PID control law is utKpbrt ytIt KpTd dyt dt Kpbrt KpyptIt where yptytTd dyt dt is the prediction of the output for time tTd Consider the proportional band yltyhtfor yptin which the corresponding u is not saturating.
For performance degradation these techniques typically evaluate anti-windup gain in terms of nonlinear L 2-induced performance level 18. E is the error signal. Anti-windup techniques Anti-windup schemes.
This technical note revisits the problem of designing a static anti-windup gain for enlarging the domain of attraction of the resulting closed-loop system by utilizing a composite quadratic Lyapunov function and an existing LMI based design algorithm is enhanced to result in a nonlinear possibly continuous anti-Windup gain. 2003 proposes a theorem that ensures the AW stability problem. The proposed scheme guarantees an H_ infty norm bound performance and system stability against the actuator saturation.
With a disturbance w t satisfying 2 we would like to design anti-windup compensators to ensure the trajectories of the closed-loop system remain bounded. Linear PI controller Fig. A is the lower limit for saturation.
Ad hoc methods Anti-windup 3. To calculate the anti-windup gain Turner et al. U k sat K p e k sat K i T s z z 1 e k A B A B s a t x A B min max x A B where.
Systems that are subject to both time-delay in state and input saturation are considered. U is the control signal. Ki is the integral gain coefficient.
Then the convex synthesis condition is derived based on the. The anti-windup gain is synthesized to enlarge the estimation of domain of attraction while guaran- teeing the stability of the closed-loop system and an optimization algorithm in the form of LMIs is constructed to compute the compensator gain which maximizes the estimation. Determine the ℒ 2 gain.
An anti-windup compensator is designed such that the robust stability of time-varying delay TS systems in the presence of control constraints is ensured and the estimate of the domain of attraction is enlarged. The design is conducted with the help of a non-quadratic Lyapunov function involving sign-indefinite quadratic forms which allows for additional degrees of freedom to be exploited for the anti-windup gain design. Using the Lemma 2 and applying in the AW-LMI synthesis it is proposed the Theorem 3 with γ a μ a.
Kp is the proportional gain coefficient. The static anti-windup compensator is in fact a nonlinear algebraic loop and its implementation needs to be robust to delay. Doyle stated the fact that any controller with slow or unstable modes will face windup problems if there are actuator constraints Doyle and Packard 1987a Doyle et al.
We design static anti-windup gains to mitigate the effect of input saturation in linear output feedback closed loops. Ts is the sampling period. Moreover the ℒ 2 -gain from the disturbance w t to the performance output z t should be minimised.
A new approach for the gain-scheduled anti-windup PID control of LPV systems is proposed in this paper. Actuator saturation integrator wind-up phenomenon discussed in detail in 6 1. Khanderia and Luyben have studied experimental evaluation of several digital algorithms for anti-reset windup Khanderia and Luyben 1976.
The LMI conditions are derived based on a chosen Lyapunov function to ensure the stability of its closed loop system and an L 2-gain performance.
Improving The Beginner S Pid Reset Windup Project Blog

Block Diagram Of The Back Calculation Anti Windup Scheme Download Scientific Diagram

Pi Controller With Back Calculation Anti Windup Scheme Download Scientific Diagram

Does Anyone Have A Suggestion Of An Anti Wind Up To This Problem
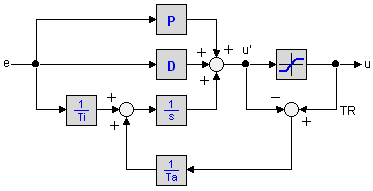
20 Sim Webhelp Library Signal Control Pid Control Anti Windup

Matlab Simulink Pid Controller Difference Between Back Calculation And Clamping For Anti Windup Stack Overflow

Discrete Time Pi Controller With External Anti Windup Input Simulink Mathworks Deutschland

Differential Pid Controller With Integrator Anti Windup Scheme And Download Scientific Diagram
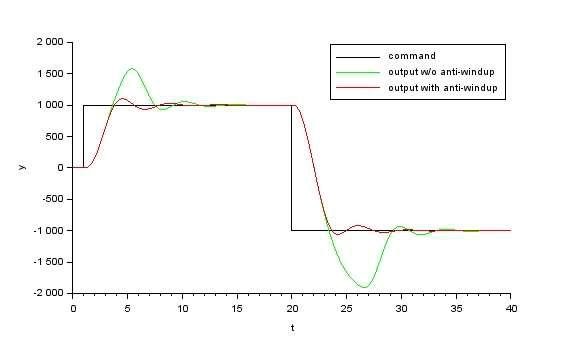
Pid Anti Windup Schemes Esi Group

Discrete Time Pi Control With Integral Anti Windup Simulink Mathworks Deutschland

3 Block Diagram Of The Pi Controller With Back Calculation Anti Windup Download Scientific Diagram

Basic Scheme For Anti Windup In A Pid Controller Download Scientific Diagram

Block Diagram Of The Back Calculation Anti Windup Scheme Download Scientific Diagram
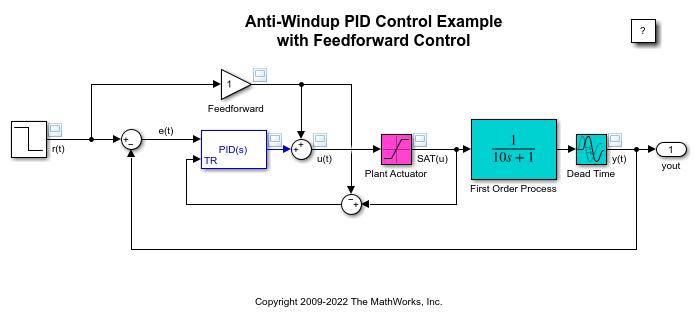
Anti Windup Control Using A Pid Controller Matlab Simulink Mathworks Deutschland

Pi Controller Structure With Anti Windup Correction Term Download Scientific Diagram

Matlab Simulink Pid Controller Difference Between Back Calculation And Clamping For Anti Windup Stack Overflow

Back Calculation Anti Windup Pid Controller Download Scientific Diagram
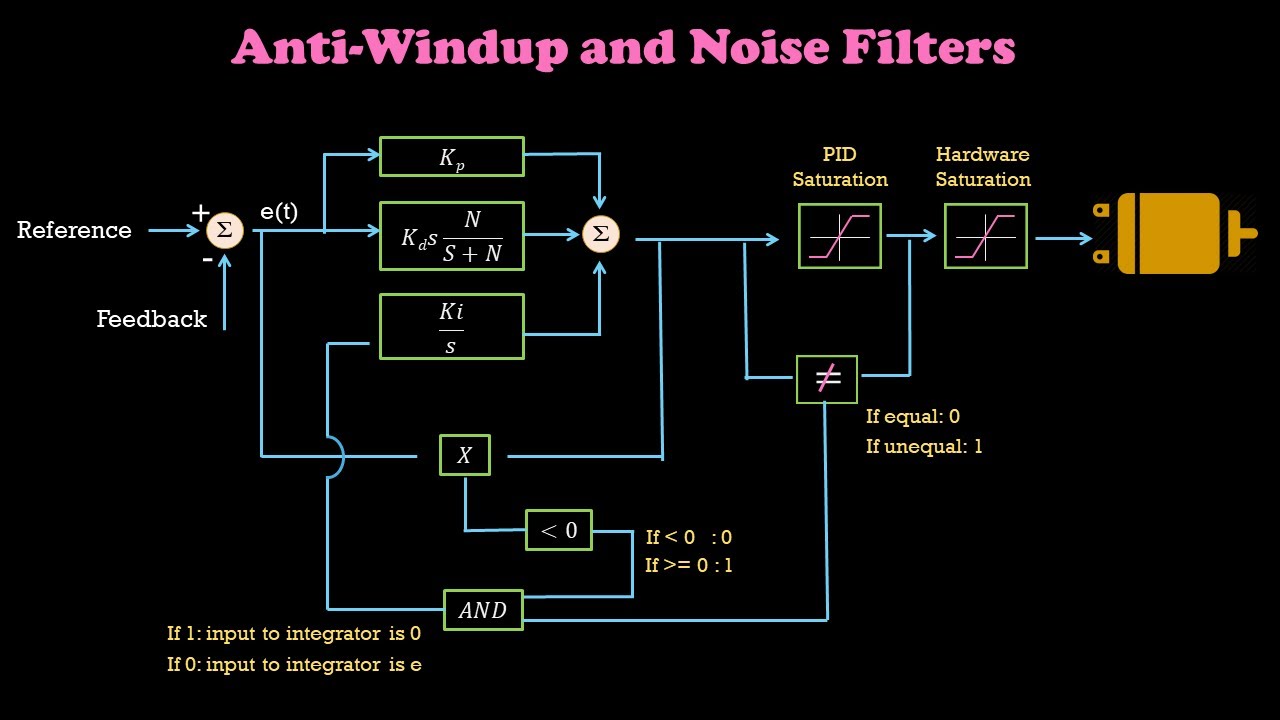
Anti Windup For Integrator And Noise Filter For Differentiator Part6 Control Systems Simplified Youtube
Comments
Post a Comment